
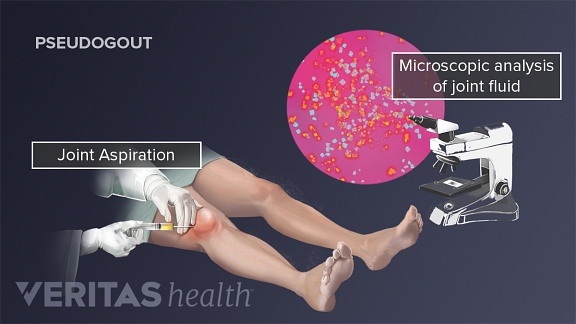

When assessing patients with any of these presentations it is important to consider the possibility of trauma, septic arthritis, Lyme disease, disseminated gonococcal infection, and autoimmune arthritis. On inspection, look for tophi whose presence usually indicates prolonged hyperuricemia and an increased likelihood of gout.Īlthough the classic gout attack is easily recognized, one should be aware of the broad differential diagnosis for both that of monoarticular and polyarticular arthritis as well as that of acute onset of severe foot pain. 1 Diagnosis is often delayed in cases with less typical presentations of gout attacks involving the wrist, elbow or when multiple joints are involved. Symptoms typically peak within the first 24 hours and resolve within 5-14 days without treatment. The classic gout attack appears as a sudden onset of pain, swelling, erythema, and warmth of the affected joint or joints. 6 In the 2015–2016 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), a stratified, multistage sample representative of the US adult population, the prevalence of self-reported, health professional-diagnosed gout was 3.9%. A community study from the United Kingdom described a 7% prevalence of chondrocalcinosis in knee x-rays of 1727 subjects, with a strong association with age. Lastly, pseudogout may be asymptomatic with the sole clinical manifestation as chondrocalcinosis incidentally noted on imaging. Additionally, pseudogout can masquerade as osteoarthritis, gout, rheumatoid arthritis and neuropathic type joint disease. Definitive diagnosis of gout and pseudogout relies on crystal examination from fluid which is not commonly performed. The prevalence of gout and pseudogout are difficult to estimate for several reasons. 4 Knees and wrists are most often involved, but other joints may be affected, including the symphysis pubis, hips, shoulders, ankles, and spine. It affects older adults, but unlike gout, it involves men and women equally. 5 These hyaline and/or fibrocartilage deposits have given rise to the use of chondrocalcinosis as an additional name of the condition, especially on x-ray reports. 3,4 It is thought that overproduction of inorganic pyrophosphate anions causes CPP crystals deposition in articular cartilage, fibrocartilage and sometimes in ligaments. Pseudogout is a similar type of arthritis resulting from crystal deposition of calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) and is also known as calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease. Comorbidities associated with hyperuricemia include obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2-diatetes mellitus, hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Non-modifiable risk factors for gout include older age, male gender, post-menopausal women, congenital errors in purine metabolism (i.e., Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome), and African American ethnicity. 1 An acute attack can be precipitated by physiological stressors such as situations causing a relatively rapid rise in uric levels including acute illness, myocardiac infarction, stroke, surgery, rapid volume changes, diuretics, large consumption of alcohol or purine rich foods, and low-dose aspirin can lead to a relatively rapid rise in uric acid levels precipitating an acute gout attack. Uric acid is excreted via the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, with approximately 65% of uric acid excreted renally. red meats, shellfish, high fructose, liver, and alcohol), uric acid overproduction and/or decreased excretion of uric acid. Hyperuricemia can result from uric acid accumulation, especially with purine rich diet (i.e. However, both monoarticular and polyarticular arthritis is possible with affected joints including ankles, knees, hands, wrist and elbows and thus, sometimes gout is overlooked as the etiology of joint pain.ĭeposition of MSU crystals occur when uric acid levels change rapidly, usually in the setting of hyperuricemia (serum uric acid level greater than 6.9 mg/dL). The classic attack occurs in the first metatarsal phalangeal joint (podagra).

Deposition of crystals leads to an acute inflammatory response and this monoarticular synovitis cause severe pain, swelling, redness and tenderness. Gout is a disease of purine metabolism characterized by acute, subacute, and chronic arthritis, due to deposits of needle shaped monosodium urate (MSU) crystals in joints, tendons, and subcutaneous tissues.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
